Periodontics
Periodontics is responsible for treating the periodontium, which includes the supporting tissues of the tooth: gums, bone tissue, cementum, and periodontal ligament. The loss of the periodontium can have several causes, but the most common is periodontal diseases caused by bacterial infections. Gum diseases, known as periodontal diseases, are - along with cavities - major dental problems in adults and the leading cause of tooth loss.
Periodontal Diseases
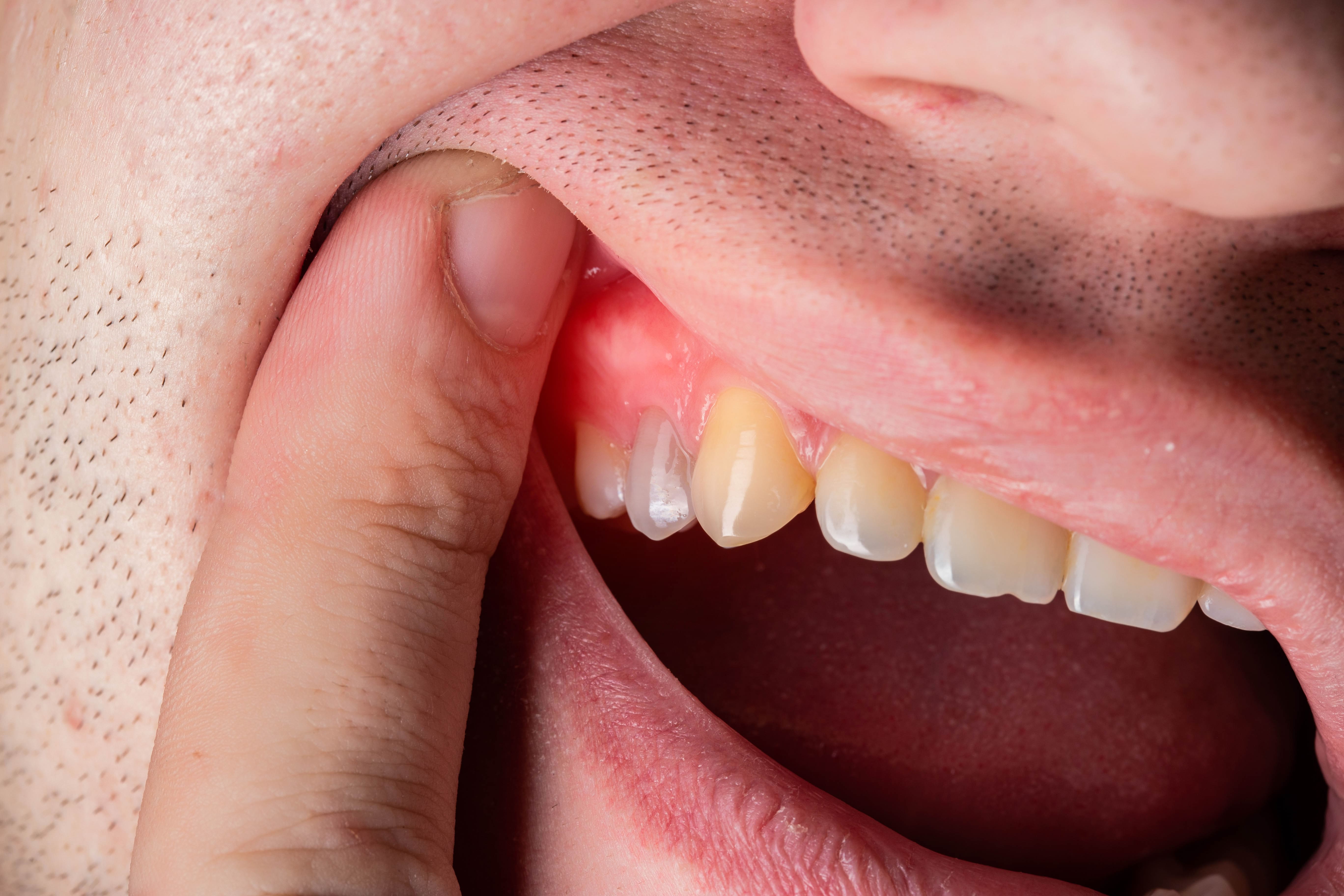
Periodontal diseases are pathological conditions affecting the supporting tissues of the teeth, caused by the accumulation of bacteria along the gum line around the teeth. They need to be treated to avoid complications such as gum swelling, recurring bleeding, loose teeth, and in extreme cases, tooth loss.
Root Planing
Root planing is a treatment method for periodontitis. In cases of periodontal disease, inflammation causes the gum to separate from the root surface, creating a space called a periodontal pocket, which allows bacteria to settle and multiply.
Root planing aims to thoroughly clean the root surfaces to remove dental plaque and tartar not only from the root surfaces but also from inside the periodontal pockets. This helps eliminate the bacteria that cause gum disease and, over time, lead to bone loss around the teeth.
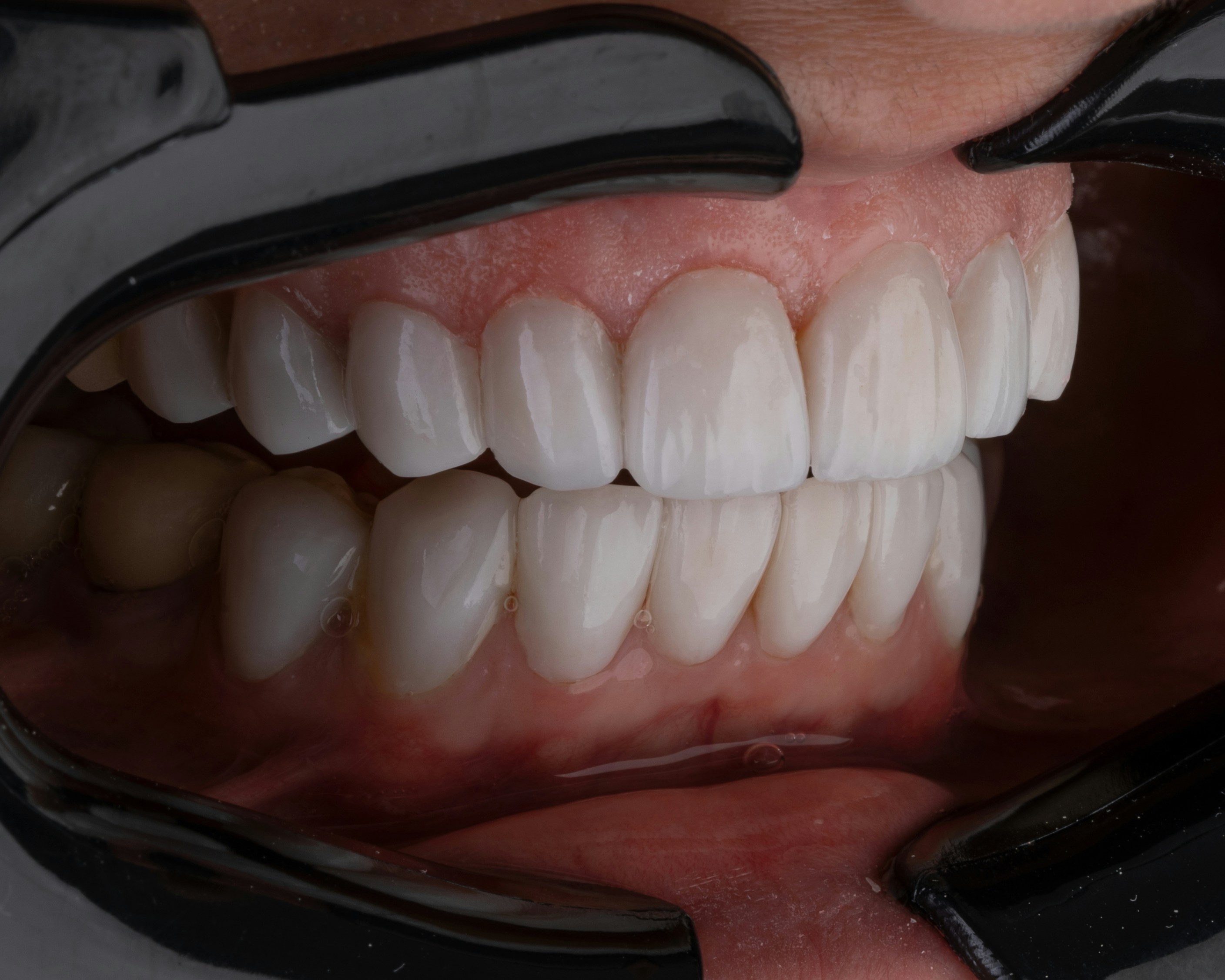
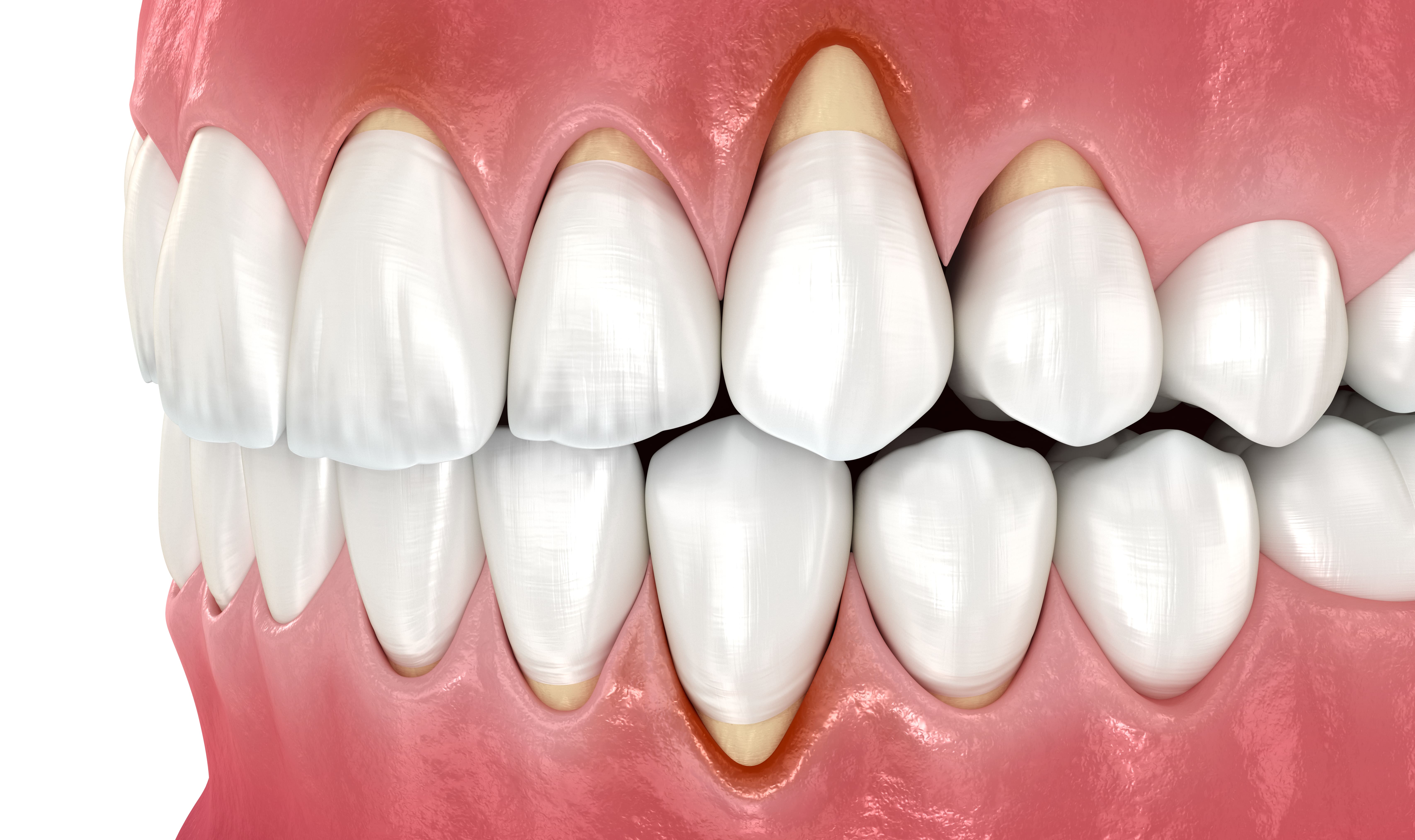
Gum Graft
Gum grafting is a very important treatment in certain clinical cases to help preserve teeth for a long time, reduce severe tooth sensitivity, and also to correct aesthetic issues caused by gum recession.
Primarily performed in highly visible areas of the mouth, especially around the front teeth, this surgical technique covers or reinforces the tooth root and provides excellent aesthetic results, particularly in terms of long-term tooth preservation.