Dental Care
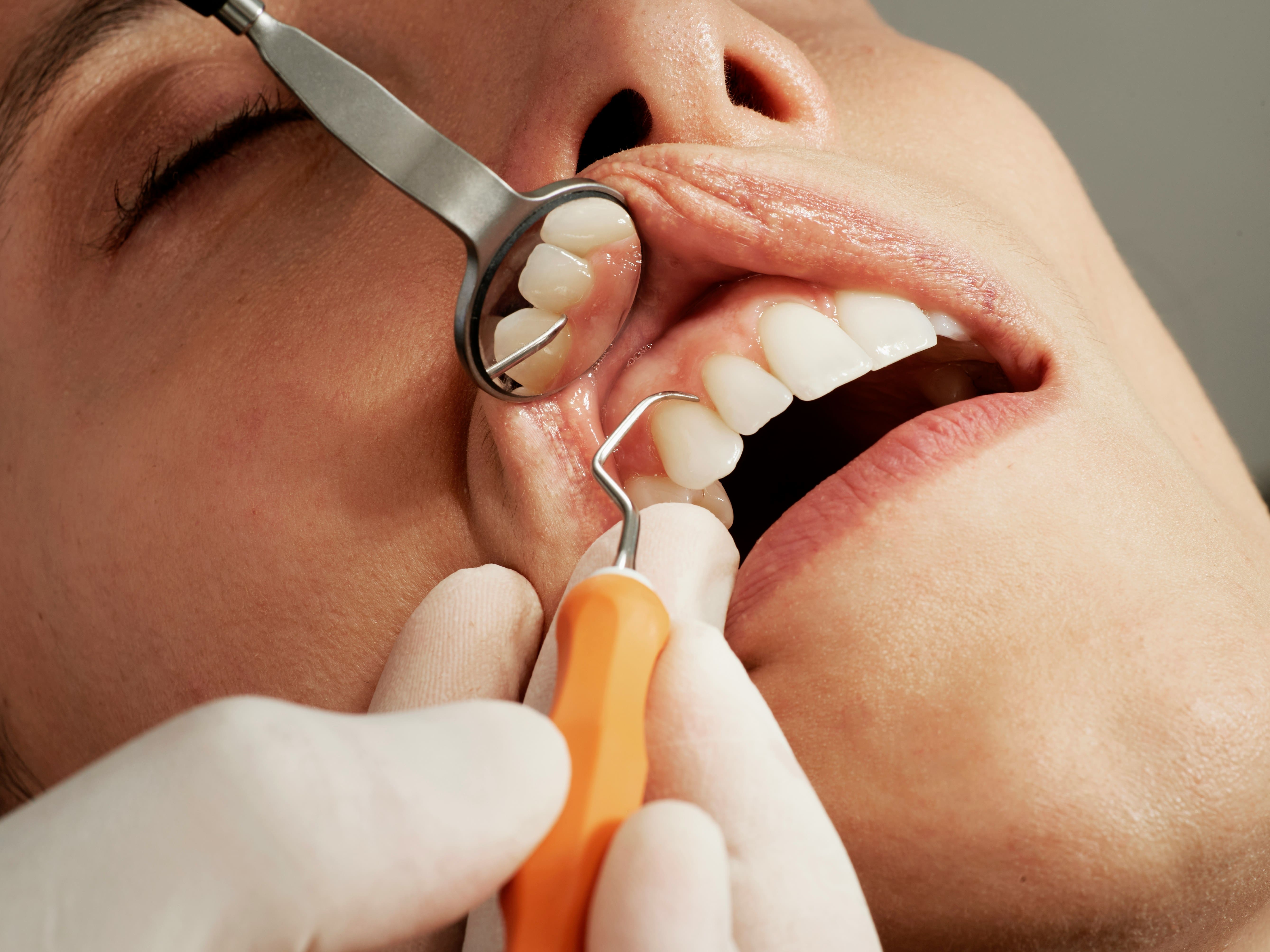
Our DENTAPTE dental centers are equipped with state-of-the-art medical technology to offer a wide range of dental treatments. Depending on your specific issue, our teams of dental surgeons will welcome you, listen to you, and advise you on the best solutions tailored to your condition.
There are many dental treatments, each designed for a specific situation: check-up visits, scaling, fillings, sealants, simple dressings, extractions, root canals (endodontics), and dental prostheses.
It is important to visit a dentist at least once a year for a dental check-up to prevent minor issues from worsening and requiring more complex treatments to restore your teeth.
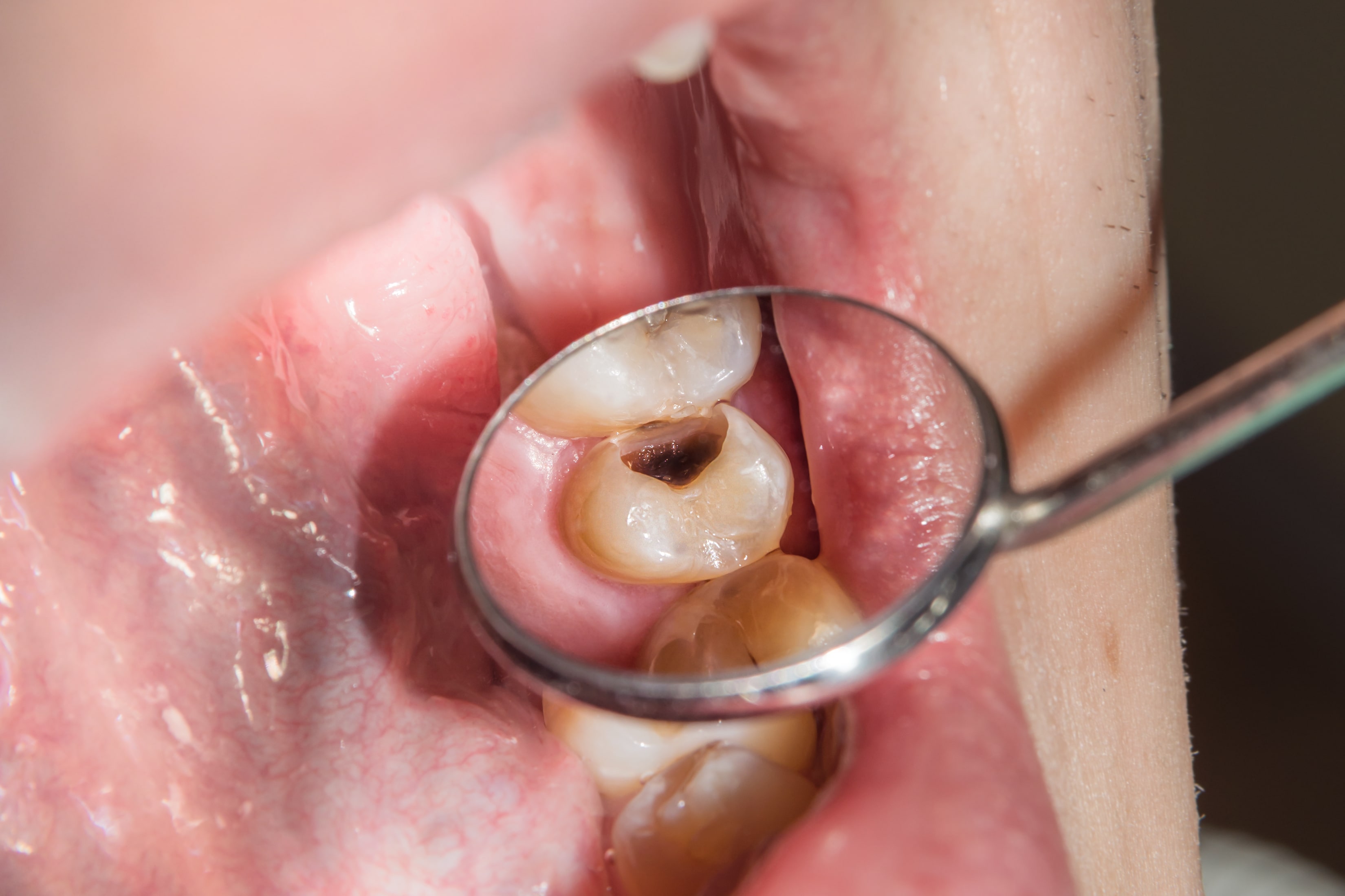
Tooth decay is an infectious disease that can affect a tooth to varying degrees depending on its stage of progression. The enamel is usually the first part affected since it covers the tooth and is the most superficial layer. The cavity begins to form and is painless at the start; however, over time, a hole develops in the tooth, and the decay spreads deeper, with early symptoms appearing.
Restorative Dentistry
Restorative dentistry involves treating the dental tissues (enamel and dentin). Caries, fractures, enamel malformations, etc., are various conditions that affect teeth at all ages and can often be repaired with simple restorations. Damaged and/or infected dental tissues are removed and replaced with the chosen material to restore the tooth structure.
Endodontics
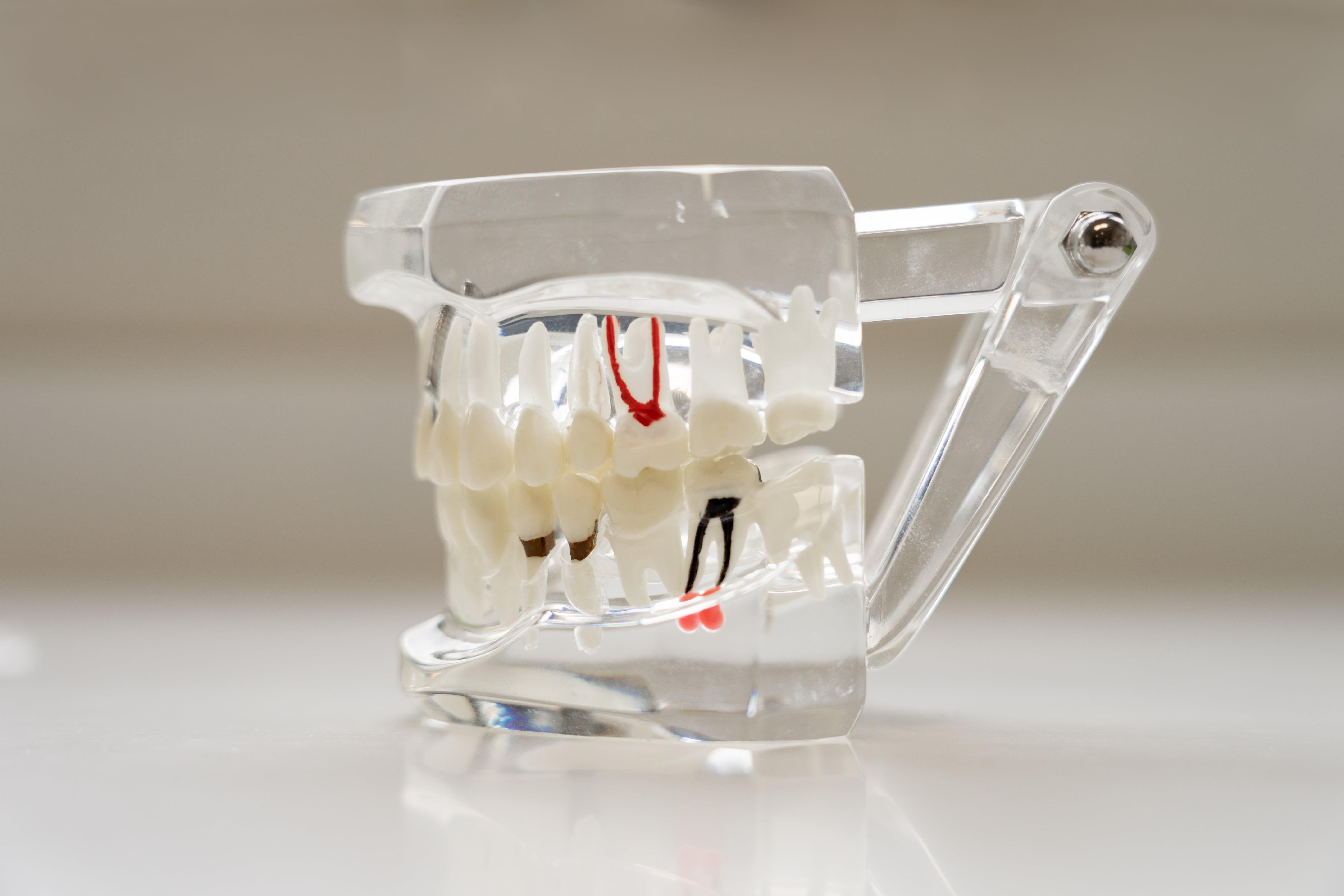
Endodontics is the discipline focused on treating the inside of the tooth, the pulp, when it is affected (by decay, fracture, necrosis, etc.). Specialists in this field are responsible for the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of periapical infections and diseases related to the dental pulp. Pulp damage is a common source of pain and, if untreated, can lead to the development of a dental abscess.
A dental surgeon performs root canal treatment (devitalization) when a tooth is infected and can no longer be preserved alive.
Tooth Extraction
Sometimes, teeth must be removed due to advanced decay, bone disease in the jaw, or trauma to the tooth. Removing a tooth is called an extraction or dental avulsion, and it is truly the last resort for the dental surgeon to resolve the issue and prevent it from spreading to other teeth.
When a tooth is extracted, it’s normal for changes to occur in your mouth. You should consult your dentist to consider solutions to avoid repeating the same issue and to replace the missing tooth.
I had a tooth pulled. What should I do now?
Avoid consuming hot drinks or foods. Prefer cold or lukewarm water and soft foods.
Be careful not to bite the inside of your cheek while it is still numb.
Avoid chewing on the affected side.
If resting, try to keep your head elevated the first night by adding an extra pillow, if possible.
Do not rinse your mouth or spit for the first 48 hours to avoid dislodging the blood clot, which is essential for proper healing.
Maintaining good oral hygiene is also important after an extraction. However, be gentle when cleaning near the extraction site.
If you are bleeding, do not rinse your mouth. Apply pressure directly to the extraction site using a cotton gauze, tissue, or similar material.
These precautions help reduce the risk of complications and promote faster healing.